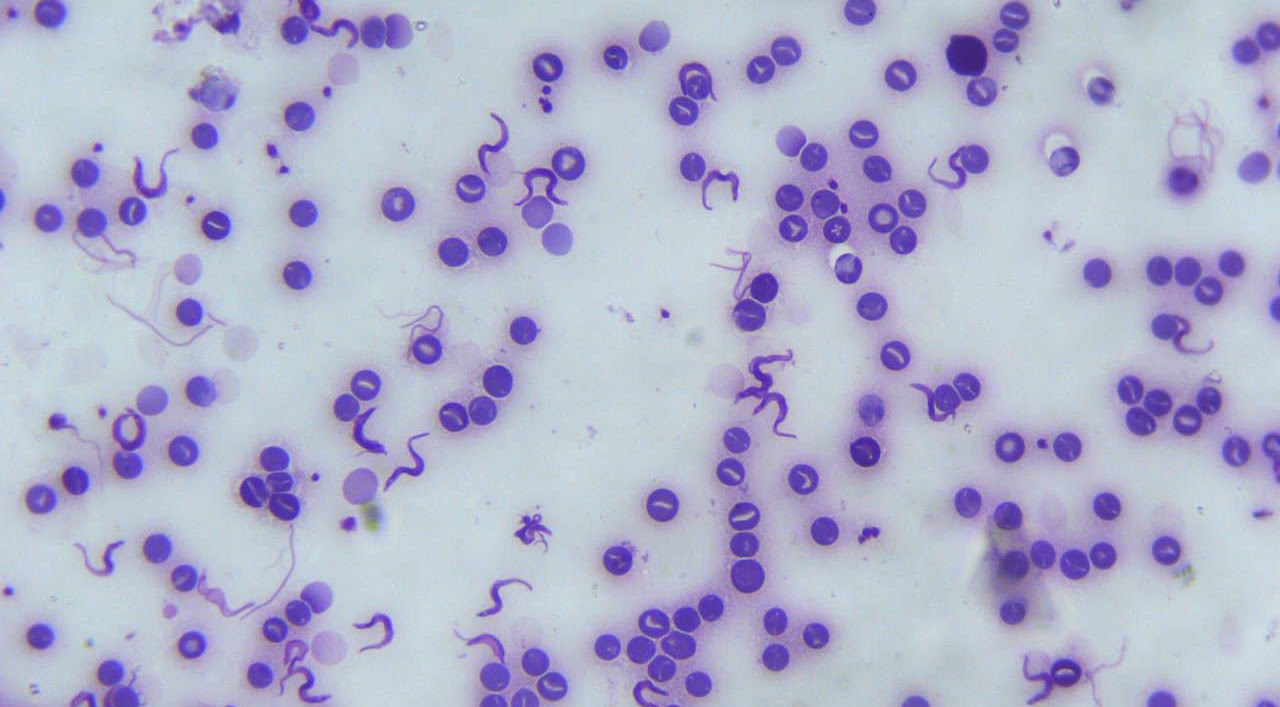
Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei is a species of protist, protozoa, parasite that is mainly found in the blood and it causes the African trypanosomiasis (or the sleeping disease) in humans and animals (nagana) in Africa. There are three subspecies of this parasite:
- T. b. gambiense, which causes the slow starting chronic trypanosomiasis.
- T. b. rhodesiense, which causes the fast starting acute tripanosomiasis.
- T. b. brucei, which causes African animal trypanosomiasis, just like other species of trypanosoma.
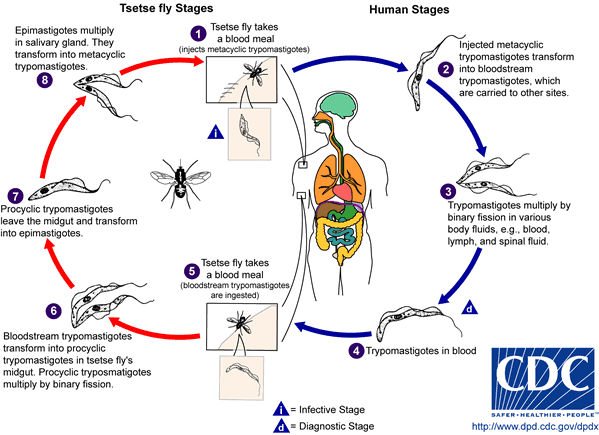
The two-host parasite species, an insect vector (the tsetse fly) and a mammal host. Given the big difference between these two hosts, the cell goes through complex changes to favor its survival in the intestine of the insects and in the blood of the mammals.
Apoyo a acciones de Innovación Docente – Vicerrectorado de Estudios / Consultas e incidencias técnicas- Tlf: 96 522 2059 –