Skin microbiota
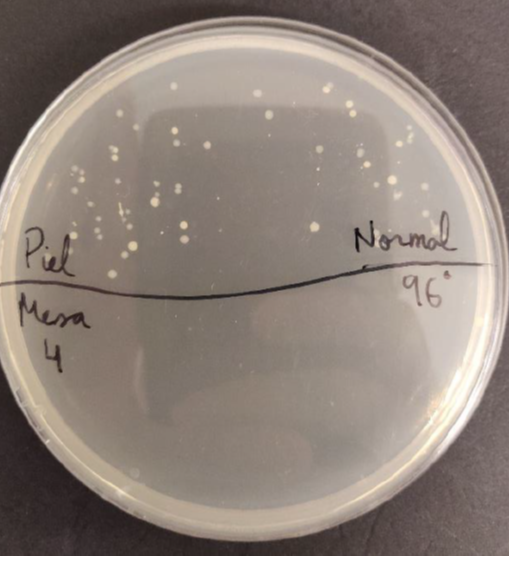
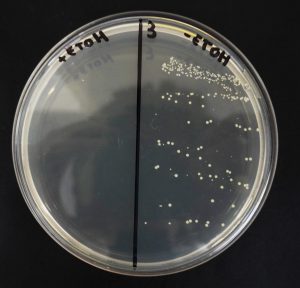
Take a sample of the forearm or the area behind the ear with a sterile swab and inoculate half of a plate with a MSA (Mannitol Salt Agar) culture medium, which is a selective culture medium for Staphylococcus. Then apply a disinfectant (alcohol) on this area and take another sample with a new swab in the other half of the plate.
Incubate everything at 37ºC for 24 hours and then observe the type of colonies and see whether the medium has changed color.
Staphylococcus aureus grows by forming yellow colonies when the mannitol is used, which produces acid and it changes the color of the culture medium, while the Staphylococcus epidermidis does not use mannitol and therefore no color change is observed.
The results are shown in the photo below, in which there are growth differences before and after the treatment with alcohol.
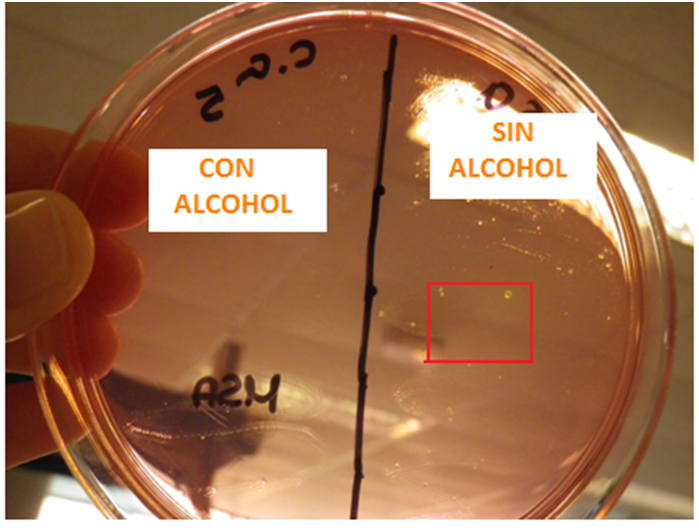
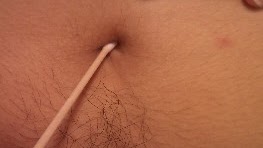
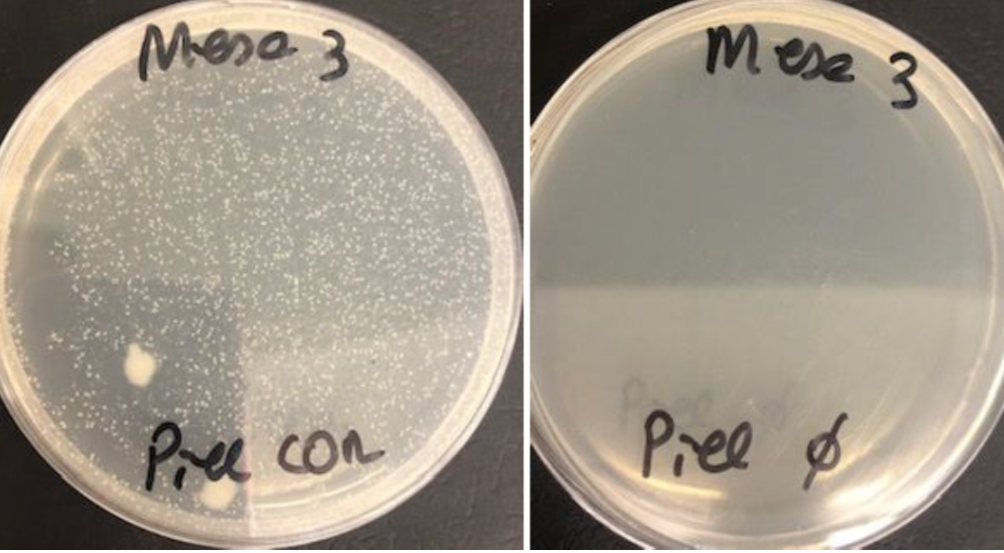
The students must also take a sample of under the nails and of the belly button with two sterile swabs (see photos) and inoculate each of the samples on the half of the other MSA plate.
It is also incubated at 37ºC for 24 hours and the possible results are observed.
Different results in which the presence of both S. aureus (yellow color) and S. epidermidis (pink color) are shown.
Apoyo a acciones de Innovación Docente – Vicerrectorado de Estudios / Consultas e incidencias técnicas- Tlf: 96 522 2059 – Skin microbiota