Visualization in agarose gel
Objective:
See the PCR product in an agarose gel that is exposed to an electric field.
Overview:
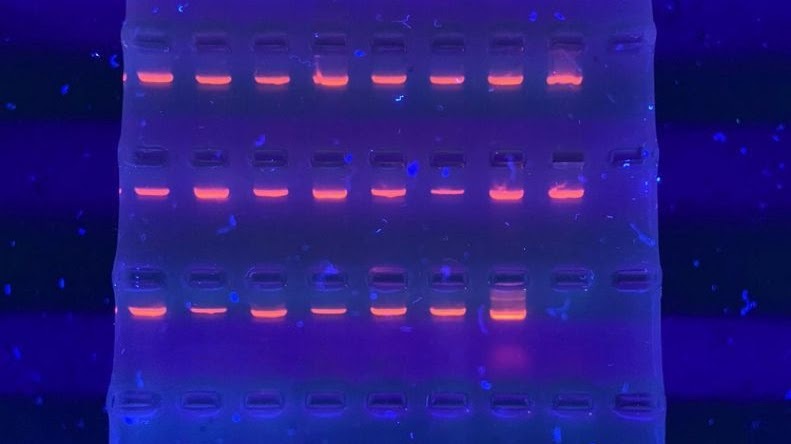
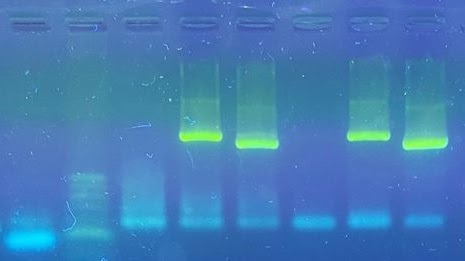
The amplified DNA fragments are negatively charged, which means that when they are exposed to an electric field (electrophoresis in agarose gel), they will migrate to the positive pole according to the size of the fragment. The smaller the fragment of DNA the faster it will move through the agarose gel.
Carrying out the practical:
To see the amplified fragments in the PCR, 1.8% agarose gel that contains coloring for the DNA is used. Each lab bench puts a sample of the PCR product (10 µl) in one of the loading wells of the agarose gel, after mixing it with 2µ from DNA gel loading buffer so that the DNA does not float and it leaves the loading wells. One loading well is kept aside for the marker of molecule sizes, which is the ruler to measure the size of the fragments moving around.
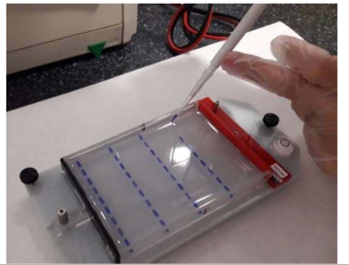
Agarose gel
Once the gel has been loaded it is exposed to an electric field for 30 minutes and then it is observed using ultraviolet light.
The amplified fragments will appear to be like bands that stay at different heights according to the size of each one. Different coloring can be used to observe the DNA. This intercalates between the bases and when it is put under light with the right wavelength the bands are seen.
Apoyo a acciones de Innovación Docente – Vicerrectorado de Estudios / Consultas e incidencias técnicas- Tlf: 96 522 2059 –